Curriculum Night & Elective Fair
Thank You to everyone who attended. Please review some of the information shared on January 23, 2024.
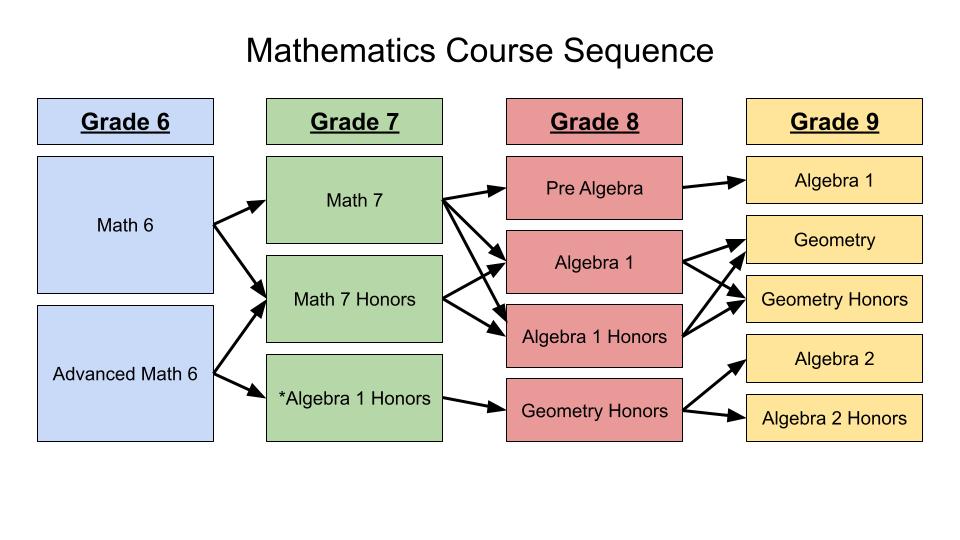
Mathematics
Areas of Focus from Math 7
(For Math 6 to Math 7 Honors)
Students enrolling in Math 7 Honors who have completed Math 6 as 6th graders will be learning 8th grade standards. Below are some of the 7th grade standards students will “skip” when they enroll in Math 7 Honors from Math 6. These “Areas of Focus” can help families determine what skills their students may need additional support in learning as they transition to Math 7 Honors.
Standard 7.3
The student will solve single-step and multistep practical problems, using proportional reasoning.
Areas of Focus:
Write and solve a proportion to find a missing value.
- Apply proportional reasoning to solve a practical problem, including scale drawings.
- Solve a problem involving tips, tax, and discounts.
Standard 7.10
The student will
determine the slope, m, as rate of change in a proportional relationship between two quantities and write an equation in the form y = mx to represent the relationship;
graph a line representing a proportional relationship between two quantities given the slope and an ordered pair, or given the equation in y = mx form where m represents the slope as rate of change.
determine the y-intercept, b, in an additive relationship between two quantities and write an equation in the form y = x + b to represent the relationship;
graph a line representing an additive relationship between two quantities given the y-intercept and an ordered pair, or given the equation in the form y = x + b, where b represents the y-intercept; and
make connections between and among representations of a proportional or additive relationship between two quantities using verbal descriptions, tables, equations, and graphs.
Areas of Focus:
- Make connections between and among representations of a linear relationship in the form y = mx or y = x + b. Representations include verbal descriptions (including practical problems), tables, equations, and graphs.
- Understand and apply the terms slope and y-intercept to a linear relationship in the form y = mx or y = x + b.
- Write an equation to represent a linear relationship in the form y = mx or y = x + b.
- Graph a line given an equation in the form y = mx or y = x + b.
Standard 7.11
The student will evaluate algebraic expressions for given replacement values of the variables.
Areas of Focus:
- Substitute a replacement value for a variable and simplify using the order of operations.
- Expressions include absolute value, brackets, and square roots of perfect squares.
Standards 7.12 and 7.13
The student will solve two-step linear equations in one variable, including practical problems that require the solution of a two-step linear equation in one variable.
Areas of Focus:
- Solve a two-step equation.
- Equations include rational coefficients and numerical terms.
- Write and solve a two-step equation to represent a practical problem.
The student will solve one- and two-step linear inequalities in one variable, including practical problems, involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, and graph the solution on a number line.
Areas of Focus:
- Solve a one-step inequality with multiplication or division, including a negative coefficient.
- Solve a two-step inequality.
- Inequalities include rational coefficients and numerical terms.
- Write and solve a one- or two-step inequality to represent a practical problem.